Sinoright Blog
The Physiological Effects of Glycine
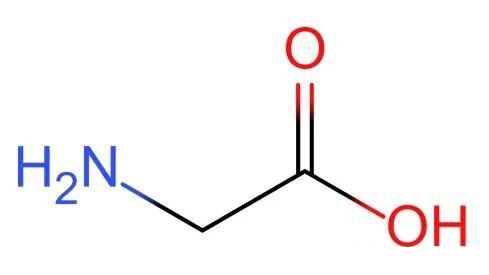
Glycine, also known as aminoacetic acid, is the most basic substance that makes up proteins. Glycine is the second most widely present amino acid found in human enzymes and proteins.
Glycine is one of the 20 amino acids used to produce proteins in the body, which can be used to construct tissues that form organs, joints, and muscles.
In the body, it is concentrated in collagen (the most abundant protein in humans and many mammals) and gelatin (a substance made from collagen).
Glycine can promote better muscle growth, heal the inner walls of the gastrointestinal tract, and slow down the loss of cartilage in joints and skin.
The Physiological Effects of Gycine
Glycine, an amino acid, is crucial for many different muscle, cognitive, and metabolic functions. It helps to break down and transport nutrients such as glycogen and fat for cells to use as energy. During this process, support the muscles, immune system, digestive system, and nervous system.
Protection of Muscles and Joints
Glycine is considered an "anti-aging amino acid" because it helps maintain lean muscle mass into old age, stimulates the secretion of growth hormone in the body, prevents joint cartilage loss, helps inhibit the degradation of valuable protein tissue that forms muscles and promotes muscle recovery, regulates the ratio of fat to muscle, and controls energy expenditure.
About one-third of collagen is composed of glycine, and collagen is crucial for forming connective tissue that keeps joints flexible and able to withstand impact. Glycine is crucial for the formation of elastic and resilient cartilage, which helps to heal damaged joints and prevent elderly people from losing mobility and function.
Cleaning and Maintenance of the Gastrointestinal Tract

Glycine helps to form the two most important substances that make up the intestinal wall: collagen and gelatin. It helps people with food allergies and sensitivities to tolerate food more easily, can soothe the inner walls of the gastrointestinal tract in patients with inflammatory bowel disease or indigestion, and even promote the balance and growth of probiotics.
In the gastrointestinal tract, glycine also plays a role in metabolizing fuel. It requires the production of bile, nucleic acid, phosphocreatine, and porphyrin to break down nutrients in the diet.
Aging Delay and Cancer Prevention
Glycine helps to form glutathione, a valuable antioxidant that can be used to prevent cell damage and various signs of aging.
In some studies, it has been found that glycine helps prevent cell mutations that lead to cancer, inhibit cancer cell growth, and suppress inflammation.
Some evidence suggests that supplementing with glycine may help reduce hypertension in patients with metabolic syndrome or those at risk of heart disease.
Cognitive and Neural Regulation
Research has shown that glycine is beneficial for cognitive ability and the central nervous system, as it plays a role in the metabolic synthesis of certain nutrients used by the brain and nerves to obtain energy.
The role of glycine in neural and neurotransmitter functions can improve sleep, mental performance, physical sensation, emotion, memory, and behavior.
It can reduce excessive brain activity and even play a role in treating or preventing mental disorders, including learning disabilities, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, etc. As part of a comprehensive treatment plan for psychological/cognitive disorders, it has also been shown to reduce psychiatric symptoms, stroke, and epileptic seizures when used in conjunction with other supplements.
Anxiety and Sleep Improvement

Due to its role in the central nervous system and digestive system, the effects of glycine can include helping to increase energy levels, balance blood sugar, and prevent fatigue.
Some evidence suggests that glycine reduces anxiety and insomnia by increasing serotonin production, which is beneficial for sleep. It can be used to calm anxiety or tension, allowing you to sleep well at night.
